GMC is a manufacturer of trucks, vans, military vehicles, and SUVs marketed in North America by General Motors Company. In January 2007, GMC was GM's second-largest-selling vehicle division after Chevrolet, ahead of Pontiac. GMC vehicles are also marketed in the Middle East.
Contents
* 1 History
* 2 Similarity to Chevrolet
* 3 GMC models
o 3.1 Light-dutyTrucks
o 3.2 Medium-duty Trucks
o 3.3 Heavy-duty Trucks
o 3.4 Buses
o 3.5 Vans
o 3.6 SUVs
o 3.7 Motorhomes
o 3.8 Military Vehicles
o 3.9 Gallery
* 4 See also
* 5 References
* 6 External links
History
GMC Truck, from a 1919 advertisement
On December 22, 1901, Max Grabowsky established a company called the "Rapid Motor Vehicle Company", which developed some of the earliest commercial trucks ever designed. The trucks utilized one-cylinder engines. In 1909, the company was purchased by General Motors to form the basis for the General Motors Truck Company, from which GMC Truck was derived.
Another independent manufacturer purchased by GM that same year was Reliance Motor Car Company. Rapid and Reliance were merged in 1911, and in 1912 the marque "GMC Truck" was first shown at the New York International Auto Show. Some 22,000 trucks were produced that year, though GMC's contribution to that total was a mere 372 units.
In 1916, a GMC Truck crossed the country from Seattle to New York City in thirty days, and in 1926, a 2-ton GMC truck was driven from New York to San Francisco in five days and 30 minutes. During the Second World War, GMC Truck produced 600,000 trucks for use by the U.S. military.
In 1925, GM purchased a controlling interest in Yellow Coach, a bus manufacturer based in Chicago, Illinois which was founded by John D. Hertz. After purchasing the remaining portion in 1943, GM renamed it GM Truck and Coach Division. The Division manufactured interurban coaches until 1980. Transit bus production ended in May 1987. The Canadian plant (in London, Ontario) produced buses from 1962 until July 1987. GM withdrew from the bus and coach market because of increased competition in the late 1970s and 1980s. Rights to the RTS model were sold to Transportation Manufacturing Corporation, while Motor Coach Industries of Canada purchased the Classic design.
In 2002, GMC released a book entitled, GMC: The First 100 Years, a complete history of the company.
GMC currently manufactures SUVs, pickup trucks, vans, light-duty trucks, and medium-duty trucks. In the past, GMC also produced fire trucks, ambulances, heavy-duty trucks, military vehicles, motorhomes, and transit buses.

gmc

gmc

gmc

gmc

gmc

gmc

gmc

gmc

gmc

gmc

gmc
 cars 2011
cars 2011 cars 2011
cars 2011 cars 2011
cars 2011 cars 2011
cars 2011 cars 2011
cars 2011 cars 2011
cars 2011 cars 2011
cars 2011 cars 2011
cars 2011 cars 2011
cars 2011 cars 2011
cars 2011 cars 2011
cars 2011 cars 2011
cars 2011 cars 2011
cars 2011 cars 2011
cars 2011 cars 2011
cars 2011
 gmc
gmc gmc
gmc gmc
gmc gmc
gmc gmc
gmc gmc
gmc gmc
gmc gmc
gmc gmc
gmc gmc
gmc gmc
gmc
 ford
ford ford
ford ford
ford ford
ford ford
ford ford
ford ford
ford ford
ford ford
ford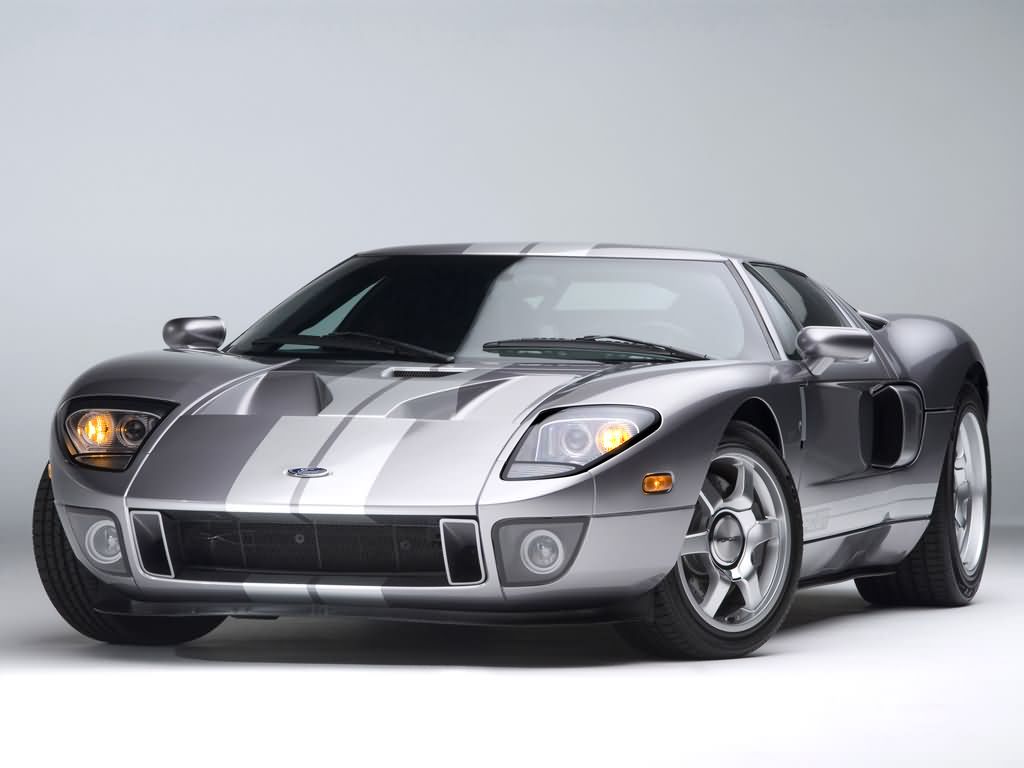 ford
ford